Otoscopes & Ophthalmoscopes
Otoscope
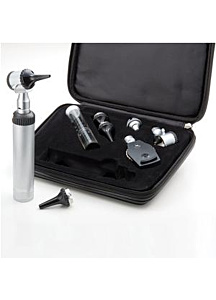
The Otoscope is a medical instrument used by health care providers to inspect the external ear. Also known as the Auriscope, these devices allow the physician to see and diagnose inflammation or swelling of the ear canal or eardrums, monitor symptoms of the outer and middle ear as well as look for illness, injury, infection or other sources of ear pain. Otoscopes that are part of a diagnostic set, such as the—ADC Standard Otoscope Ophthalmoscope Diagnostic Set—are frequently used to examine patients’ noses and upper throats as well. The ADC Pocket Otoscope Ophthalmoscope Diagnostic Set is another available option.
Some otoscopes are wall-mounted while others are portable. The head of the otoscope contains a a light source and a low-power magnifying lens. These enable the physician to see in and around the ear. The front of the otoscope is covered by a disposable plastic piece which assists in the positioning of the ear canal for a clearer examination. The Alaris Medical Systems Disposable Probe Covers allows for fast temperature readings in oral, axillary, and rectal body sites. They are easily disposable and safe for the regular garbage.
The Otoscopic, Auditory Examination:
The patient will sit and tilt their head away from the physician so the ear not being examined is close to their shoulder. This angle opens the side of the head, giving the physician greater access to the ear being examined. Children will often lie on their sides or lean their heads against an adult"s chest during the exam.
They health care provider will lightly pull on the outer ear to adjust the position and direction of the ear canal; straightening it, for a better view. The physician will then move the otoscope around the ear canal. This allows the examiner to see different angles inside the ear and improves their view in the event of ear wax blockage.
These tests are conducted whenever infection, inflammation, chronic or acute ear infection or another condition such as Cholsteatoma, a head injury, or a ruptured or perforated eardrum is suspected. They are often performed as part of a routine check-up as well.
The Anatomy of the Ear:
The External Ear is responsible for collecting sound. It is composed of the Helix, Trangular Fossa, External Auditory Meaths, Tragus, Antitragus and Lobule.
The Middle Ear works to transmit sound and equalize pressure. It is composed of three small auditory bones: Malleus, Incus, Stapes; as well as the tympanic membrane (eardrum) and the Eustachian Tubue.
The Inner Ear houses the Cochlea, which is the auditory organ. It is composed of a membranous, curved cavity.